Lipids and Cholesterol
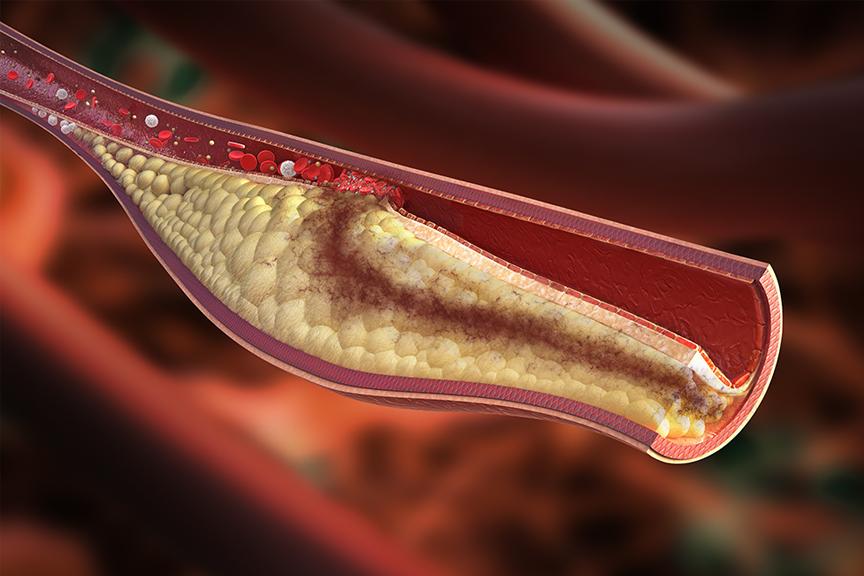
Hyperlipidemia is an umbrella term that refers to any of several acquired or genetic disorders that result in a high level of lipids (fats, cholesterol and triglycerides) circulating in the blood. The term hyperlipidemia can cover many conditions, but for most people, it comes down to two well-known terms: high cholesterol and high triglykerides.
Our bodies produce and use a certain amount of lipids every day, but sometimes that system gets out of whack, either because of a genetic predisposition or because of a high fat diet and a sedentary lifestyle. The excess lipids build up in the walls of our arteries and increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can lead to carotid artery disease and stroke, coronary disease and heart attack and peripheral vascular disease and need for amputation. The risk of atherosclerosis is even higher if you smoke, if you have diabetes, high blood pressure and/or kidney failure.
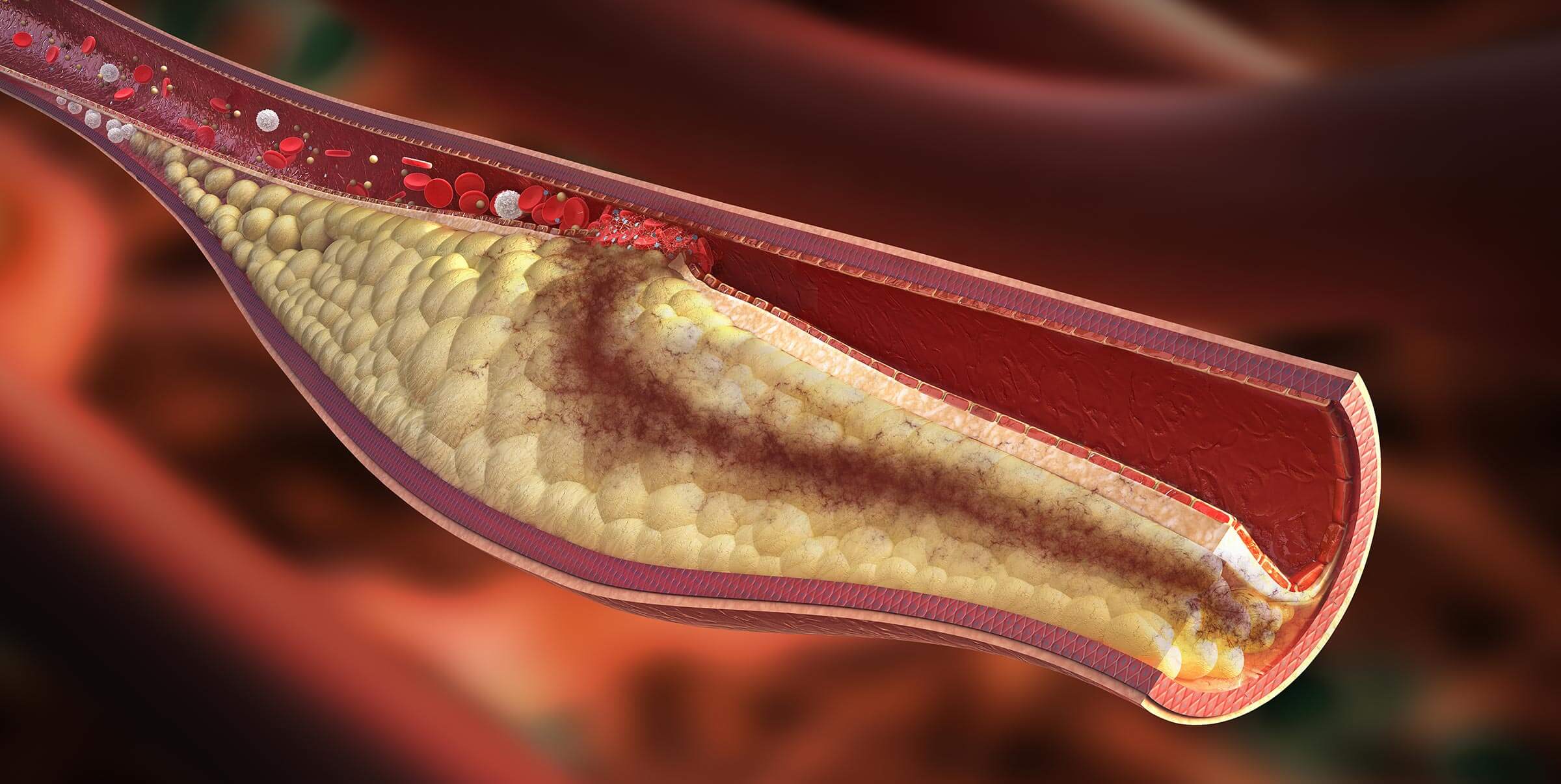
Hyperlipidemia itself does not cause symptoms, other than slowly and silently generating atherosclerosis. Your doctor will usually recommend blood tests to monitor your lipids and recommend lifestyle changes and medical therapy as needed.
Regardless of the cause of elevated blood lipids, the important therapeutic goal is to reduce them. For people who have mild to moderate elevations and no other cardiovascular disease risk factors (including family history of hyperlipidemia), lifestyle changes alone may be enough to bring lipid levels down to acceptable ranges. When lipid levels remain elevated despite lifestyle changes, or the person cannot make adequate lifestyle changes, health experts recommend lipid-lowering medications.
Consulting a doctor is important, since each condition has it quirks. For people with high triglycerides, for example, alcohol can be particularly dangerous. But for those with high cholesterol, a daily glass of wine or other alcohol, along with healthy eating and exercise, may actually help.
 Understanding Cholesterol
Understanding CholesterolCholesterol is a waxy substance critical to the normal function of all cells. The body needs cholesterol for making hormones, digesting dietary fats, building cell walls, and other important processes...Read more
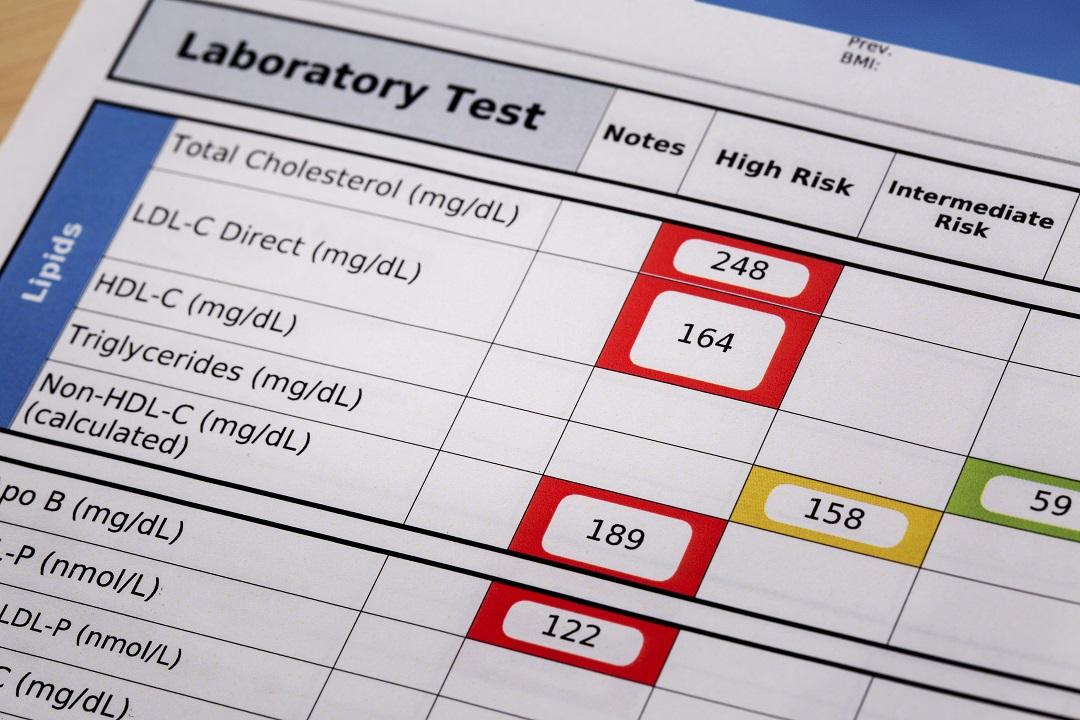 Cholesterol Numbers that Matter
Cholesterol Numbers that Matter
Many people do not know their cholesterol is too high because there are usually no symptoms. Keeping your cholesterol levels healthy is a great way to keep your heart, your brain and your legs healthy...Read more
 Controlling High Cholesterol
Controlling High Cholesterol
Making healthy eating choices and increasing exercise are important first steps in improving your cholesterol. For some people, particularly for those that high cholesterol runs in their family, cholesterol-lowering medication...Read more
 Medical Treatment (Statins)
Medical Treatment (Statins)When diet and exercise alone are not enough to reduce cholesterol to goal levels, doctors often prescribe anti-cholesterol medications (statins). Statins taken orally, usually once a day, are extremely effective in lowering LDL...Read more
 Triglycerides
Triglycerides
Triglyceride is the most common type of lipid in the body and it is stored in fat tissue. Only a small portion of your triglycerides is found in the bloodstream. Triglykerides are not cholesterol...Read more
Swollen Legs

Venous Insufficiency, Lymphedema, Fluid Retention or What Else?
Leg swelling generally occurs because of an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the lower extremity. The medical term for leg swelling from excessive fluid in the tissues is peripheral edema. Symptoms that can be associated with leg swelling include leg pain, numbness, redness, itching, rash, shortness of breath, thickening and ulceration of the skin.

Common causes of leg swelling include:
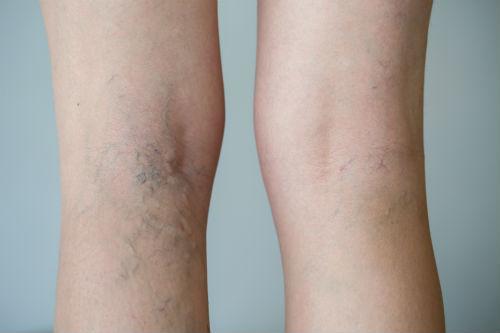 Venous insufficiency / Varicose Veins
Venous insufficiency / Varicose Veins
Venous insufficiency is the inability or difficulty of the leg veins to return blood back to the heart. As the blood pools in the leg it leads to heaviness and swelling at the end of the day...Read more
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Swollen legs are a common problem during pregnancy. For many women, their legs become more and more swollen as the pregnancy advances...Read more
 Leg infection
Leg infection
Leg infection usually referred as cellulitis can be a usual cause of swelling and it has distinct characteristics. Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and the tissues beneath...Read more
 Heart failure
Heart failure
Congestive heart failure is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of your heart muscles. While often referred to simply as “heart failure,” congestive heart failure...Read more
 Salt / Water retention
Salt / Water retention
The body's balance of salt is usually well-regulated. Most people can consume salt in the diet without concern for developing salt depletion or retention...Read more
 Drug side effects
Drug side effects
Many medicines can cause edema, including...Read more
 Blood clots (Venous Thrombosis)
Blood clots (Venous Thrombosis)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition wherein a blood clot develops in one of our "deep" veins, blocking the venous blood flow. Symptoms can range between a simple leg swelling to a fatal pulmonary embolism...Read more
 Lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema refers to swelling that generally occurs in one or both of your or legs. Lymphedema is related to a disorder (usually acquired, rarely congenital) of your lymphatic system (lymphatic vessels and lymphnodes)...Read more
 Kidney disease
Kidney disease
When you have kidney disease, fluid and sodium may not be removed appropriately thus retained in your body. The edema associated with kidney disease usually occurs in your legs and around your eyes...Read more
 Liver disease
Liver disease
Severe liver disease (such as cirrhosis) causes retain fluid retention. Cirrhosis slows the normal flow of blood through the liver, thus increasing pressure in the veins that bring blood from the intestines and spleen to the liver...Read more
 Thyroid disease
Thyroid disease
Thyroid disorders, mainly hypothyroidism (e.g. Hashimoto’s) but hyperthyroidism (e.g. Graves disease) too, can cause face and leg swelling. It’s often felt as leg pain along with swelling, itching...Read more
 Trauma
Trauma
An ankle sprain is a usual cause of lower leg swelling. It is a painful injury to the ankle ligaments and normally happens when the ankle is turned or twisted. Swelling, tenderness, and bruising are common symptoms...Read more
 Idiopathic (unknown)
Idiopathic (unknown)
Idiopathic edema or idiopathic lymphedema is a common cause of fluid retention and swelling most usual in women under the age of 50. "Idiopathic" means that the cause of this condition is unknown...Read more
Varicose Veins: Laser Treatment
Endovenous ablation with either laser or radiofrequency, has largely replaced the traditional surgery (vein "stripping") in the management of venous insufficiency. It is usually used for the great or small saphenous veins, or any other superficial vein that may be insufficient. Both laser and radiofrequency ablation are essentially similar procedures with similar outcomes and risks.
Page 3 of 3