Carotid endarterectomy is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for carotid artery disease.
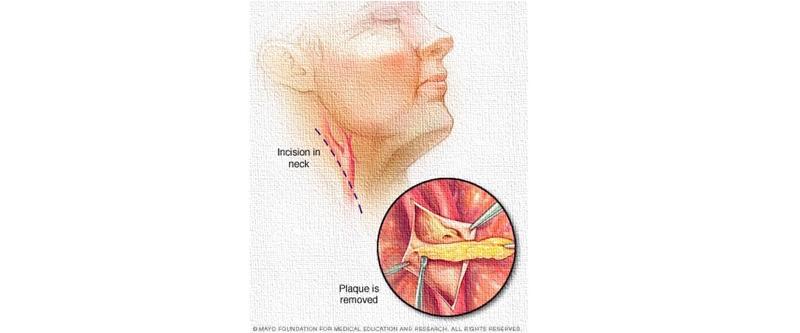
While the patient is under general anesthesia, an small incision is made in the neck at the location of the blockage.
The surgeon isolates and opens the carotid artery to remove the atherosclerotic plaque. Then, the artery is sewn back together to allow improved blood flow to the brain.
Typically patients who undergo this procedure have a supervised hospital stay for one day after surgery.
While the operation can result in some post-operative neck pain, most of this can be relieved with standard pain medications.
As with any operation, carotid endarterectomy has a risk of minor and major complications, the most serious one being the risk of stroke.
You will want to discuss them thoroughly with your vascular surgeon.
