Hyperlipidemia is an umbrella term that refers to any of several acquired or genetic disorders that result in a high level of lipids (fats, cholesterol and triglycerides) circulating in the blood. The term hyperlipidemia can cover many conditions, but for most people, it comes down to two well-known terms: high cholesterol and high triglykerides.
Our bodies produce and use a certain amount of lipids every day, but sometimes that system gets out of whack, either because of a genetic predisposition or because of a high fat diet and a sedentary lifestyle. The excess lipids build up in the walls of our arteries and increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can lead to carotid artery disease and stroke, coronary disease and heart attack and peripheral vascular disease and need for amputation. The risk of atherosclerosis is even higher if you smoke, if you have diabetes, high blood pressure and/or kidney failure.
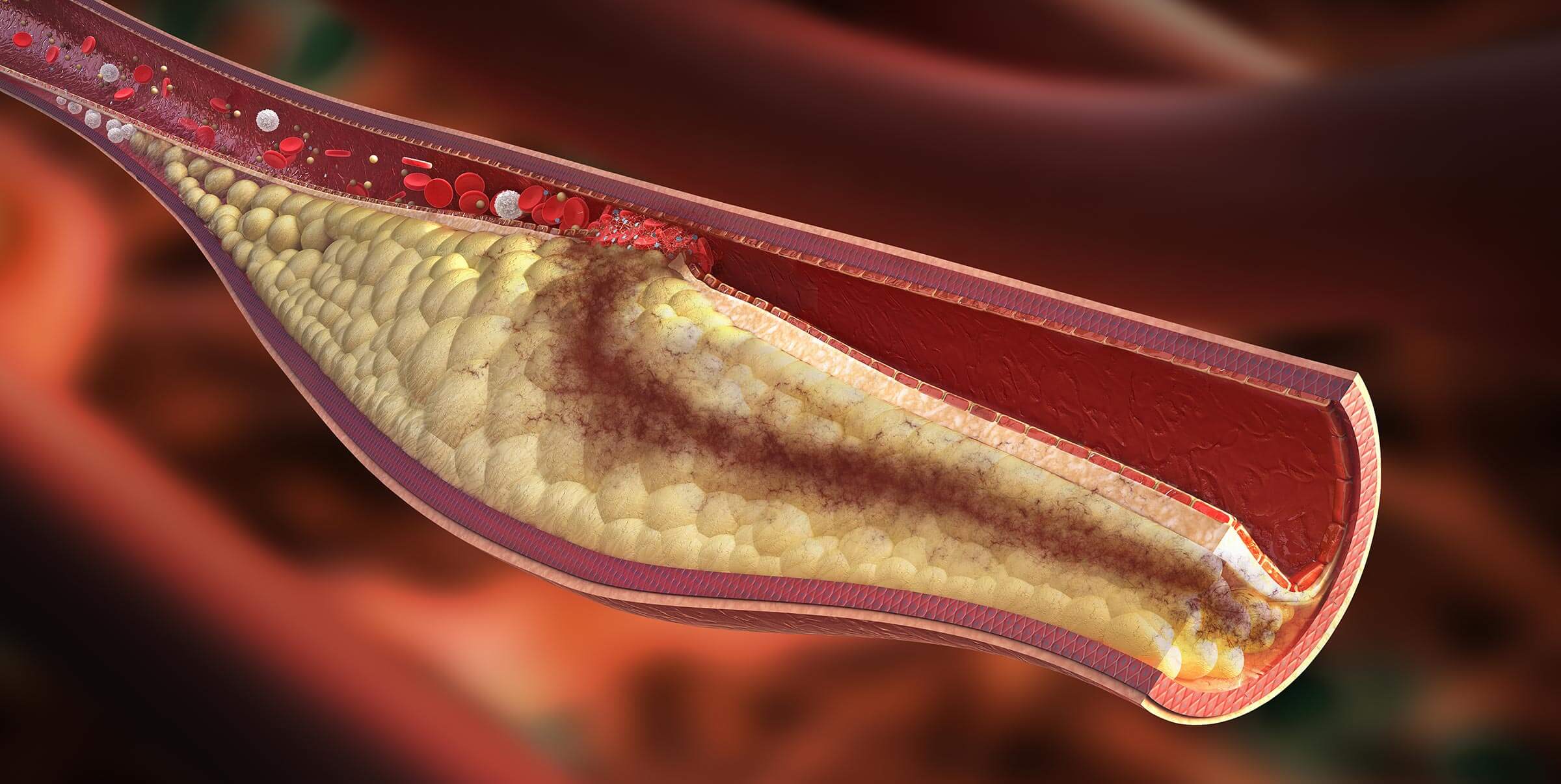
Hyperlipidemia itself does not cause symptoms, other than slowly and silently generating atherosclerosis. Your doctor will usually recommend blood tests to monitor your lipids and recommend lifestyle changes and medical therapy as needed.
Regardless of the cause of elevated blood lipids, the important therapeutic goal is to reduce them. For people who have mild to moderate elevations and no other cardiovascular disease risk factors (including family history of hyperlipidemia), lifestyle changes alone may be enough to bring lipid levels down to acceptable ranges. When lipid levels remain elevated despite lifestyle changes, or the person cannot make adequate lifestyle changes, health experts recommend lipid-lowering medications.
Consulting a doctor is important, since each condition has it quirks. For people with high triglycerides, for example, alcohol can be particularly dangerous. But for those with high cholesterol, a daily glass of wine or other alcohol, along with healthy eating and exercise, may actually help.
 Understanding Cholesterol
Understanding CholesterolCholesterol is a waxy substance critical to the normal function of all cells. The body needs cholesterol for making hormones, digesting dietary fats, building cell walls, and other important processes...Read more
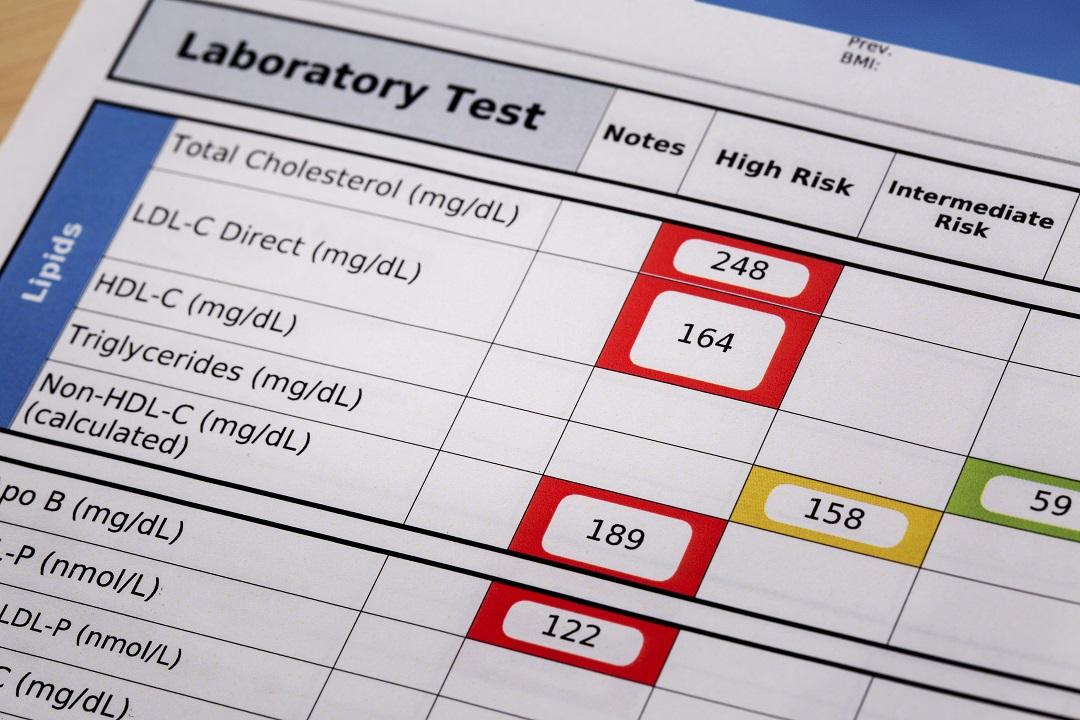 Cholesterol Numbers that Matter
Cholesterol Numbers that Matter
Many people do not know their cholesterol is too high because there are usually no symptoms. Keeping your cholesterol levels healthy is a great way to keep your heart, your brain and your legs healthy...Read more
 Controlling High Cholesterol
Controlling High Cholesterol
Making healthy eating choices and increasing exercise are important first steps in improving your cholesterol. For some people, particularly for those that high cholesterol runs in their family, cholesterol-lowering medication...Read more
 Medical Treatment (Statins)
Medical Treatment (Statins)When diet and exercise alone are not enough to reduce cholesterol to goal levels, doctors often prescribe anti-cholesterol medications (statins). Statins taken orally, usually once a day, are extremely effective in lowering LDL...Read more
 Triglycerides
Triglycerides
Triglyceride is the most common type of lipid in the body and it is stored in fat tissue. Only a small portion of your triglycerides is found in the bloodstream. Triglykerides are not cholesterol...Read more
